Word Macro Examples & VBA Tutorial
Written by
Reviewed by
In this Article
Welcome to our Word VBA / Macros Mega-Guide!
This page contains:
-
- Word VBA Tutorial PDF (Free Download)
- Word VBA “Cheat Sheet” containing a list of the most commonly used Word VBA code snippets
- Full Word VBA / Macro tutorial.
- Searchable list of all of our Word VBA Macro Tutorials
You might also be interested in our Interactive VBA Tutorial for Excel. While some of the examples / exercises are specific to Excel VBA, much of the content is generic to all VBA and you may find it useful to learn concepts like If Statements, Loops, MessageBoxes, and more.
VBA PDF (Free Downloads)
Download our free Microsoft Word VBA Tutorial! Or VBA Tutorials for other Office Programs!
Word VBA Examples “CheatSheet”
Below you will find simple VBA code examples for working with Microsoft Word.
Select / Go To
Selection.Extend
Selection.MoveLeft Unit:=wdCharacter, Count:=1
Bookmarks
.Add Range:=Selection.Range, Name:=”Name”
.DefaultSorting = wdSortByName
.ShowHidden = False
End With
n = ActiveDocument.Bookmarks.Count
‘Do something
End If
Selection.Delete Unit:=wdCharacter, Count:=1
Selection.InsertAfter “New Text”
ActiveDocument.Bookmarks.Add Range:=Selection.Range, _
Name:=”BookmarkName”
Document
Set doc = Documents.Add
NewTemplate:=False
Columns
varNumberPages = _
ActiveDocument.Content.Information(wdActiveEndAdjustedPageNumber)
Font
Insert
Selection.Range.InsertAutoText
Loops
‘Do Something
Sub
ForEach doc In Documents
‘Do Something
Next doc
Dim i As Long, iParCount As Long
iParCount = ActiveDocument.Paragraphs.CountFori = 1 To iParCount
ActiveDocument.Paragraphs(i).Alignment = wdAlignParagraphLeft
Next i
Paragraph
.LineSpacingRule = wdLineSpaceExactly
.LineSpacing = 12
End With
Dim i As Long, iParCount As Long
iParCount = ActiveDocument.Paragraphs.CountFori = 1 To iParCount
ActiveDocument.Paragraphs(i).Alignment = wdAlignParagraphLeft
Next i
Word VBA Macro Tutorial
This is a tutorial for using VBA with Microsoft Word. This tutorial will teach you how to write a simple Macro and interact with Documents, Ranges, Selections, and Paragraphs.
Note: If you’re brand new to Macros / VBA you might also find this article useful: How to write VBA Macros from Scratch.
VBA is the programming language used to automate Microsoft Office programs including Word, Excel, Outlook, PowerPoint, and Access.
Macros are blocks of VBA code that perform specific tasks.
When you Record a Macro, Word will write VBA code into a Macro, allowing you to repeat your actions. You can see a list of all available Macros from View > Macros.
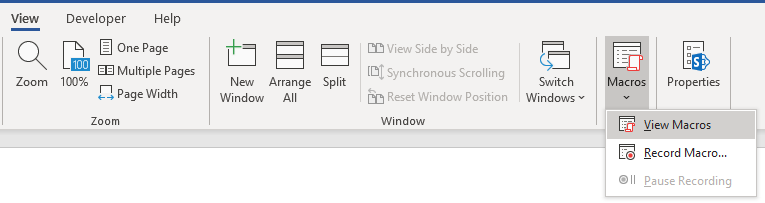
After recording a Macro, you will be able to edit the Macro from the Macro List:
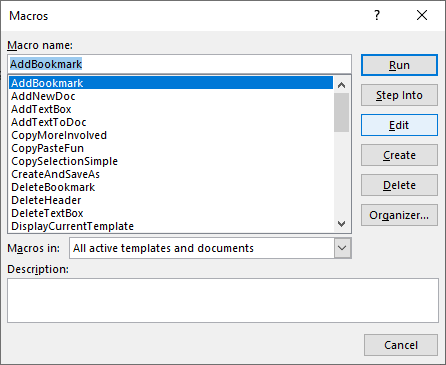
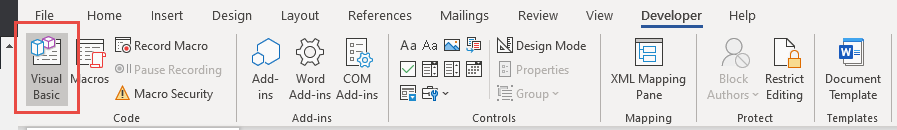
When you click Edit, you open the VBA Editor. Using the VBA Editor you can edit recorded Macros or write a Word Macro from scratch. To access the VBA Editor use the shortcut ALT + F11 or click Visual Basic from the Developer Ribbon.
Simple Word Macro Example
This is a simple example of a Word VBA Macro. It performs the following tasks:
- Opens a Word Document
- Writes to Document
- Closes and Saves the Word Document.
Sub WordMacroExample()
'Open Doc & Assign to Variable
Dim oDoc As Document
Set oDoc = Documents.Open("c:\Users\someone\NewDocument.docx")
'Write To Doc
Selection.TypeText "www.automateexcel.com"
Selection.TypeParagraph
'Save and Close Doc
oDoc.Save
oDoc.Close
End SubWord Macro Basics
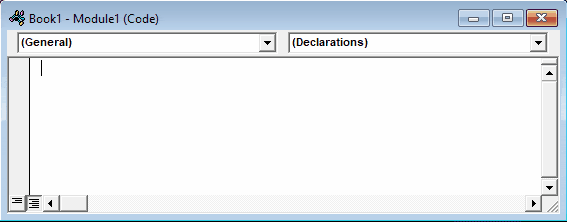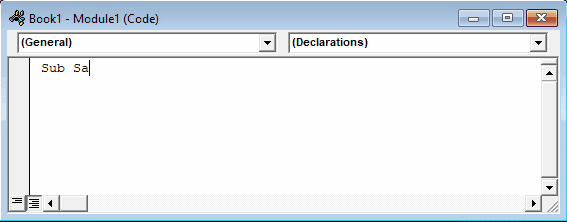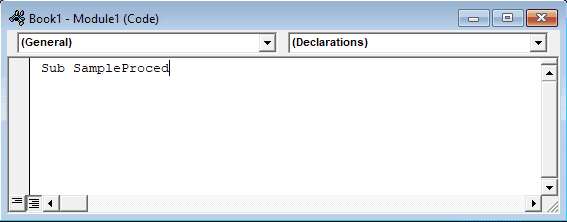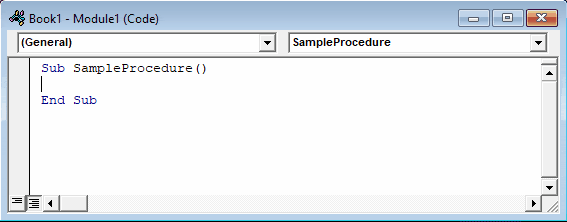
All VBA code must be stored within procedures like this. To create a procedure in VBA type “Sub WordMacroExample” (Where “WordMacroExample” is your desired Macro name) and press ENTER. VBA will automatically add the parenthesis and End Sub.
Word Document Object
When interacting with Microsoft Word in VBA, you will frequently reference Word “Objects”. The most common objects are:
Application Object – Microsoft Word itself
Document Object – A Word document
Range Object – A part of a Word document
Selection Object – A selected range or cursor location.
Application
Application is the “top-level” object. All other objects in Word can be reached through it.
In addition to accessing other Word objects, there are “application-level” settings that can be applied:
Application.Options.AllowDragAndDrop = TrueThis is an example of accessing the “Selection” of “Windows(1)” with in the Application:
Application.Windows(1).Selection.Characters.CountHowever, the most common Word objects can be accessed directly, without typing the full hierarchy. So instead, you can (and should) just type:
Selection.Characters.CountDocuments
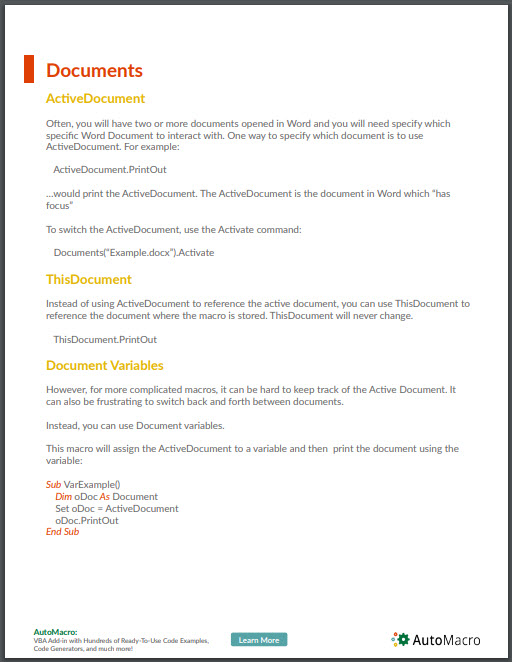
ActiveDocument
Often, you will have two or more documents opened in Word and you will need specify which specific Word Document to interact with. One way to specify which document is to use ActiveDocument. For example:
ActiveDocument.PrintOut…would print the ActiveDocument. The ActiveDocument is the document in Word which “has focus”
To switch the ActiveDocument, use the Activate command:
Documents("Example.docx").ActivateThisDocument
Instead of using ActiveDocument to reference the active document, you can use ThisDocument to reference the document where the macro is stored. ThisDocument will never change.
ThisDocument.PrintOutDocument Variables
However, for more complicated macros, it can be hard to keep track of the Active Document. It can also be frustrating to switch back and forth between documents.
Instead, you can use Document variables.
This macro will assign the ActiveDocument to a variable and then print the document using the variable:
Sub VarExample()
Dim oDoc As Document
Set oDoc = ActiveDocument
oDoc.PrintOut
End SubDocument Methods
Open Document
To Open a Word Document:
Documents.Open "c:\Users\SomeOne\Desktop\Test PM.docx"We recommend always assigning a Document to a variable upon opening it:
Dim oDoc as Document
Set oDoc = Documents.Open("c:\Users\SomeOne\Desktop\Test PM.docx")Create New Document
To create a new Word Document:
Documents.AddWe can instruct Word to create a new doc based on some template:
Documents.Add Template:="C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Templates\MyTemplate.dotx"As always, it is useful to assign document to variable upon creating or opening:
Dim oDoc as Document
Set oDoc = Documents.Add (Template:="C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Templates\MyTemplate.dotx")Save Document
To save a document:
ActiveDocument.Saveor SaveAs:
ActiveDocument.SaveAs FileName:= c:\Users\SomeOne\Desktop\test2.docx", FileFormat:=wdFormatDocumentClose Document
To close a Document and save changes:
ActiveDocument.Close wdSaveChangesor without saving changes:
ActiveDocument.Close wdDoNotSaveChangesPrint Document
This will print the active Document:
ActiveDocument.PrintOutRange, Selection, Paragraphs
Range and Selection are probably the most important objects in Word VBA, certainly the most used.
Range refers to some portion of document, usually, but not necessarily, text.
Selection refers to selected text (or other object like pictures) or, if nothing is selected, an insertion point.
Paragraphs represent paragraphs in document. Its less important than it sounds, because you can’t directly access paragraph text (you need to access particular paragraph range to make modifications).
Range
Range can be any part of document, including entire document:
Dim oRange As Range
Set oRange = ActiveDocument.Contentor it can be small as one character.
Another example, this range would refer to first word in document:
Dim oRange As Range
Set oRange = ActiveDocument.Range.Words(1)Usually, you would want to get range which refers to specific part of document and then modify it.
In the following example we will make the first word of second paragraph bold:
Dim oRange As Range
Set oRange = ActiveDocument.Paragraphs(2).Range.Words(1)
oRange.Bold = TrueSet Range Text
To set the text value of a Range:
Dim oRange As Range
Set oRange = ActiveDocument.Paragraphs(2).Range.Words(1)
oRange.Text = “Hello ”(Tip: Note the space after “Hello”. Because word object includes space after word, with just “hello” we would get “Hellonext word”)
There are hundreds of things which you can do with ranges. Just a few examples (these assume you are already made object variable oRange referring to range of interest):
Change font
oRange.Font.Name = "Arial"Display in message box number of characters in particular range
MsgBox oRange.Characters.CountInsert some text before it
oRange.InsertBefore "this is inserted text "Add a footnote to range
ActiveDocument.Footnotes.Add Range:=oRange, _
Text:="Read more at automateexcel.com."Copy it to clipboard
oRange.Copy
Often you need to change to what is particular range referring. So you can start it’s start and end
oRange.Start = 5
oRange.End = 50After above code, oRange would refer to text starting with fifth and ending with 50th character in document.
Selection
Selection is even more widely used than Range, because it is easier to work with Selections than Ranges, IF your macro ONLY interacts with the ActiveDocument.
First select the desired part of your document. For example select the second paragraph in active document:
ActiveDocument.Paragraphs(2).Range.SelectThen you can use the Selection Object to type some text:
Selection.TypeText "Some text"We can type some paragraphs bellow “Some text”:
Selection.TypeText "Some text"
Selection.TypeParagraphOften, it’s necessary to know if some text is selected or we have just a insertion point:
If Selection.Type <> wdSelectionIP Then
Selection.Font.Bold = True
Else
MsgBox "You need to select some text."
End IfWhen working with Selection object we want to place insertion point to particular place, and issue commands starting from this point.
Beginning of document:
Selection.HomeKey Unit:=wdStory, Extend:=wdMoveBeginning of current line:
Selection.HomeKey Unit:=wdLine, Extend:=wdMoveThe Extend parameter wdMove moves the insertion point. Instead, you could use wdExtend which will select all text between the current insertion point.
Selection.HomeKey Unit:=wdLine, Extend:=wdExtendMove Selection
The most useful method for changing position of insertion point is Move. To move Selection two characters forward:
Selection.Move Unit:=wdCharacter, Count:=2to move it backwards, use negative number for Count parameter:
Selection.Move Unit:=wdCharacter, Count:=-2Unit parameter can be wdCharacter, wdWord, wdLine, or more (use Word VBA help to see others).
To move words instead:
Selection.Move unit:=wdWord, Count:=2
Selection is easier to work with (compared to ranges) because it is like a robot using Word, mimicking human user. Where Insertion point is – some action would take place. But, this means that you must take care where insertion point is! This is not easy after many steps in code. Otherwise, Word would change text in not desired place.
In the case you need some property or method not available in Selection object you can always easily obtain range associated with selection:
Set oRange = Selection.RangeTIP: Using Selection is often easier than using ranges, but also it’s way slower (important when you deal with big documents)
Paragraphs
You can’t directly use Paragraphs object to change text:
ActiveDocument.Paragraphs(1).Text = "No, it wouldn't work"Above wouldn’t work (actually it will throw an error). You need to first obtain range associated with particular paragraph:
ActiveDocument.Paragraphs(1).Range.Text = "It works now :)"But you can directly change its style:
ActiveDocument.Paragraphs(1).Style = "Normal"or change its paragraph level formatting:
ActiveDocument.Paragraphs(1).LeftIndent = 10or maybe you want to keep this paragraph on the same line with next paragraph:
ActiveDocument.Paragraphs(1).KeepWithNext = TrueMake paragraph centered:
ActiveDocument.Paragraphs(1).Alignment = wdAlignParagraphCenterIt is VERY useful to assign a particular paragraph to object variable. If we assign particular paragraph to variable we don’t have to worry if the first paragraph becomes the second because we inserted one paragraph before it:
dim oPara as Paragraph
Set oPara = Selection.Paragraphs(1) ‘here we assign first paragraph of current selection to variableHere is an example where we insert a paragraph above the first paragraph, but we can still reference the old first paragraph because it was assigned to a variable:
Sub ParagraphExample()
Dim oPara As Paragraph
Set oPara = ActiveDocument.Paragraphs(1)
MsgBox oPara.Range.Text
oPara.Range.InsertParagraphBefore 'Insert Paragraph
MsgBox oPara.Range.Text
End SubParagraph object is very frequently used in loops:
Sub LoopThroughParagraphs()
Dim oPara As Paragraph
For Each oPara In ActiveDocument.Paragraphs
'do something with it. We will just display
'paragraph text if its style is "Heading 4"
If oPara.Style = "Heading 4" Then
MsgBox oPara.Range.Text
End If
Next oPara
End SubWord Templates
Current Template
This Word VBA macro will display the current template:
Sub DisplayCurrentTemplate()
'displays full path of template active document
MsgBox ActiveDocument.AttachedTemplate.FullName, , "Template location"
End SubMake New Template
This Word VBA macro will make a new template:
Sub MakeNewTemplate()
'creates a new doc and saves as a template
Dim strName As String
Dim strPath As String
Dim oDoc As Document
strPath = Options.DefaultFilePath(wdUserTemplatesPath) & Application.PathSeparator 'find where templates are stored at user's computer
strName = "Sample automateexcel.com template.dotm"
Set oDoc = Documents.Add 'create a new doc and asign it to oDoc variable
'write some text in the new doc reffering to it using oDoc variable
oDoc.Range.InsertBefore "Sample template"
oDoc.Range.InsertParagraphAfter
oDoc.Range.InsertAfter "Visit https://www.automateexcel.com/vba-code-library"
oDoc.SaveAs FileName:=strPath & strName, FileFormat:=wdFormatXMLTemplateMacroEnabled, AddToRecentFiles:=False
oDoc.Close wdDoNotSaveChanges 'close doc
End Sub
Bookmarks
Add Bookmark
This Word macro will add a bookmark:
Sub AddBookmark()
ActiveDocument.Bookmarks.Add "automateexcel_com_01"
End SubDelete Bookmark
This VBA macro will delete a bookmark:
Sub DeleteBookmark()
If ActiveDocument.Bookmarks.Exists("automateexcel_com_01") Then 'we need to check if bookmark named "automateexcel_com_01" exists in active doc
ActiveDocument.Bookmarks(Index:="automateexcel_com_01").Delete
End If
End SubGo To Bookmark
This simple macro will go to a bookmark:
Sub GoToBookmark()
If ActiveDocument.Bookmarks.Exists("automateexcel_com_01") Then 'we need to check if bookmark named "automateexcel_com_01" exists in active doc
Selection.GoTo What:=wdGoToBookmark, Name:="automateexcel_com_01"
End If
End SubModify Bookmark
This macro will modify a bookmark’s content:
Sub ModifyBookmarkContent()
' change bookmark contents
' more complicated, because changing bookmark range content will delete bookmark
Dim oRangeBKM As Range
If ActiveDocument.Bookmarks.Exists("automateexcel_com_01") Then 'we need to check if bookmark named "automateexcel_com_01" exists in active doc
'Identify current Bookmark range and insert text
Set oRangeBKM = ActiveDocument.Bookmarks("automateexcel_com_01").Range
oRangeBKM.Text = "automateexcel.com"
'Make again the bookmark
ActiveDocument.Bookmarks.Add "automateexcel_com_01", oRangeBKM
End If
End SubThis is a modify bookmark function:
Sub UpdateBookmarkContent(strBookMarkName As String, strNewText As String)
' "usable' procedure for add in
Dim oRangeBKM As Range
If ActiveDocument.Bookmarks.Exists(strBookMarkName) Then 'we need to check if bookmark named "automateexcel_com_01" exists in active doc
'Identify current Bookmark range and insert text
Set oRangeBKM = ActiveDocument.Bookmarks(strBookMarkName).Range
oRangeBKM.Text = strNewText
'Make again the bookmark
ActiveDocument.Bookmarks.Add strBookMarkName, oRangeBKM
End If
End SubYou can call the function by adding the bookmark name and new text as arguments:
Sub CallBookmarkFunction()
Call UpdateBookmarkContent("automateexcel_com_01", "automateexcel.com")
End SubTextBox
Add TextBox
This macro will add a TextBox to the active Word document:
Sub AddTextBox()
ActiveDocument.Shapes.AddTextBox Orientation:=msoTextOrientationHorizontal, Left:=1, Top:=1, Width:=300, Height:=100
End SubDelete TextBox
This VBA macro will delete the first TextBox in the active document:
Sub DeleteTextBox()
'deletes first text box in activedoc
'not straithforward because its not easy to identify text boxes
Dim oShape As Shape
If ActiveDocument.Shapes.Count > 0 Then
For Each oShape In ActiveDocument.Shapes
If oShape.AutoShapeType = msoShapeRectangle Then 'we need to check both if oShape is of type msoShapeRectangle and its textframe contains place for writing
If oShape.TextFrame.HasText = True Then
oShape.Delete
End If
End If
Next oShape
End If
End SubWrite in TextBox
This Word macro uses similar methodology to write to the first TextBox in the active document:
Sub WriteInTextBox()
'writes into first text box in active doc
Dim oShape As Shape
If ActiveDocument.Shapes.Count > 0 Then
For Each oShape In ActiveDocument.Shapes
If oShape.AutoShapeType = msoShapeRectangle Then 'we need to check both if oShape is of type msoShapeRectangle and its textframe contains place for writing
If oShape.TextFrame.HasText = True Then
oShape.TextFrame.TextRange.InsertAfter "https://www.automateexcel.com/vba-code-library"
Exit For 'we just want to write into first textbox
End If
End If
Next oShape
End If
End SubTables
Add Table to Word Document
This simple macro will add a table to your Word document:
Sub VerySimpleTableAdd()
Dim oTable As Table
Set oTable = ActiveDocument.Tables.Add(Range:=Selection.Range, NumRows:=3, NumColumns:=3)
End SubSelect Table in Word
This macro will select the first table in the active Word document:
Sub SelectTable()
'selects first table in active doc
If ActiveDocument.Tables.Count > 0 Then 'to avoid errors we check if any table exists in active doc
ActiveDocument.Tables(1).Select
End If
End SubLoop Through all Cells in a Table
This VBA macro will loop through all cells in a table, writing the cell count to the cell:
Sub TableCycling()
' loop through all cells in table
Dim nCounter As Long ' this will be writen in all table cells
Dim oTable As Table
Dim oRow As Row
Dim oCell As Cell
ActiveDocument.Range.InsertParagraphAfter 'just makes new para athe end of doc, Table will be created here
Set oTable = ActiveDocument.Tables.Add(Range:=ActiveDocument.Paragraphs.Last.Range, NumRows:=3, NumColumns:=3) 'create table and asign it to variable
For Each oRow In oTable.Rows ' outher loop goes through rows
For Each oCell In oRow.Cells 'inner loop goes
nCounter = nCounter + 1 'increases the counter
oCell.Range.Text = nCounter 'writes counter to the cell
Next oCell
Next oRow
'display result from cell from second column in second row
Dim strTemp As String
strTemp = oTable.Cell(2, 2).Range.Text
MsgBox strTemp
End SubCreate Word Table From Excel File
This VBA example will make a table from an Excel file:
Sub MakeTablefromExcelFile()
'advanced
Dim oExcelApp, oExcelWorkbook, oExcelWorksheet, oExcelRange
Dim nNumOfRows As Long
Dim nNumOfCols As Long
Dim strFile As String
Dim oTable As Table 'word table
Dim oRow As Row 'word row
Dim oCell As Cell 'word table cell
Dim x As Long, y As Long 'counter for loops
strFile = "c:\Users\Nenad\Desktop\BookSample.xlsx" 'change to actual path
Set oExcelApp = CreateObject("Excel.Application")
oExcelApp.Visible = True
Set oExcelWorkbook = oExcelApp.Workbooks.Open(strFile) 'open workbook and asign it to variable
Set oExcelWorksheet = oExcelWorkbook.Worksheets(1) 'asign first worksheet to variable
Set oExcelRange = oExcelWorksheet.Range("A1:C8")
nNumOfRows = oExcelRange.Rows.Count
nNumOfCols = oExcelRange.Columns.Count
ActiveDocument.Range.InsertParagraphAfter 'just makes new para athe end of doc, Table will be created here
Set oTable = ActiveDocument.Tables.Add(Range:=ActiveDocument.Paragraphs.Last.Range, NumRows:=nNumOfRows, NumColumns:=nNumOfCols) 'create table and asign it to variable
'***real deal, table gets filled here
For x = 1 To nNumOfRows
For y = 1 To nNumOfCols
oTable.Cell(x, y).Range.Text = oExcelRange.Cells(x, y).Value
Next y
Next x
'***
oExcelWorkbook.Close False
oExcelApp.Quit
With oTable.Rows(1).Range 'we can now apply some beautiness to our table :)
.Shading.Texture = wdTextureNone
.Shading.ForegroundPatternColor = wdColorAutomatic
.Shading.BackgroundPatternColor = wdColorYellow
End With
End SubWord VBA Tutorial Conclusion
This tutorial covered the basics of Word VBA. If you’re new to VBA, you should also review our general VBA Tutorial to learn more about Variables, Loops, MessageBoxes, Settings, Conditional Logic and much more.
Word Macro Examples
| Word Macro Examples |
|---|
| SaveAs PDF |
| Find and Find and Replace |
| Open Documents |
Count Words in Selection
This Word VBA Macro will count the number of words in the selection. If no selection is made, it will count the number of words in the entire document.
Sub WordCount()
'counts whole doc, then word Count for selection (if something is selected)
Dim nWordsCount As Long
Dim nCharCount As Long
nWordsCount = ActiveDocument.Range.ComputeStatistics(wdStatisticWords)
nCharCount = ActiveDocument.Range.ComputeStatistics(wdStatisticCharacters)
MsgBox "The entire doc contains: " & vbCrLf & nWordsCount & " words and" & vbCrLf & _
nCharCount & " characters without spaces", , "Word Count"
'now show word count for selected text
If Selection.Words.Count >= 1 And Selection.Type <> wdSelectionIP Then
nWordsCount = Selection.Range.ComputeStatistics(wdStatisticWords)
nCharCount = Selection.Range.ComputeStatistics(wdStatisticCharacters)
MsgBox "Selected text contains: " & vbCrLf & nWordsCount & " words and" & vbCrLf & _
nCharCount & " characters without spaces", , "Word Count (selection)"
End If
End Sub
Word VBA FAQs
What is a Word Macro?
A Macro is a general term that refers to a set of programming instructions that automates tasks. Word Macros automate tasks in Word using the VBA programming language.
Does word have VBA?
Yes, Microsoft Word has the VBA Editor. It can be accessed with by pressing ALT + F11 or by navigating to Developer > Visual Basic.
How do I use VBA in Word?
1. Open the VBA Editor (ALT + F11 or Developer > Visual Basic)
2. Go to Insert > Module to create a Code Module
3. Type ‘Sub HelloWorld’ and press Enter
4. In between the lines ‘Sub HelloWorld’ and ‘End Sub’, type ‘MsgBox “Hello World!’
5. You’ve created a Macro!
6. Now press ‘F5’ to run the Macro