VBA ActiveWorkbook vs. ThisWorkbook
Written by
Reviewed by
In this Article
This tutorial will discuss the difference between the VBA ActiveWorkbook and ThisWorkbook objects.
ActiveWorkbook vs. ThisWorkbook
It’s important to the know the difference between the ActiveWorkbook and ThisWorkbook in VBA:
The ActiveWorkbook is the workbook that is currently active (similar to how ActiveSheet is the currently active sheet). ThisWorkbook is the workbook where the VBA code is stored. ThisWorkbook will never change.
ThisWorkbook
Think of ThisWorkbook as an object variable that allows you to reference the workbook containing the currently running code.
This code will display a MessageBox with ThisWorkbook name:
Sub Show_ThisWorkbook()
MsgBox ThisWorkbook.Name
End Sub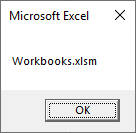
ActiveWorkbook
The ActiveWorkbook is an object variable that allows you to reference the currently active workbook.
This code will display a MessageBox with ActiveWorkbook name:
Sub Show_ActiveWorkbook()
MsgBox ActiveWorkbook.Name
End SubVBA Assumes ActiveWorkbook
When attempting to work with objects (ex. Sheets) within the ActiveWorkbook, you do not need to explicitly state the ActiveWorkbook object. VBA will assume you are referring to the ActiveWorkbook.
So this:
ActiveWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").Range("$A$5").Value = 1Is the same as this:
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("$A$5").Value = 1New or Opened Workbooks are Active
Whenever you create a new workbook or open a workbook, the workbook becomes “Active”. You can see for yourself with this code that will add a workbook and retrieve the new workbook’s name:
Sub Show_ActiveWorkbook_Add()
Workbooks.Add
MsgBox ActiveWorkbook.Name
End SubAfter adding or opening a workbook, you can assign it to a variable by using the ActiveWorkbook object. We will show you how in the examples below:
ThisWorkbook and ActiveWorkbook Examples
Switch Active Workbook
Switch the active workbook using Workbook name:
Workbooks("Book1").ActivateSwitch the active workbook using an index as a workbook order number (1 is the first workbook opened or created):
Workbooks(1).ActivateMake ThisWorkbook Active
Make ThisWorkbook (where the currently running code is stored) the ActiveWorkbook:
ThisWorkbook.ActivateSet ActiveWorkbook to a Variable
Assign the ActiveWorkbook to a workbook object variable:
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = ActiveWorkbookClose and Save the Active Workbook
Closes and Saves the ActiveWorkbook:
ActiveWorkbook.Close SaveChanges:=TrueClose the Active Workbook Without Saving
Closes the ActiveWorkbook without saving:
ActiveWorkbook.Close SaveChanges:=FalseActiveWorkbook – Save As
Performs a Save As of the active Workbook.
Sub SaveAsActiveWorkbook()
Dim result As Variant
result = Application.GetSaveAsFilename(InitialFileName:="", _
FileFilter:="Excel Macro-Enabled Workbook (*.xlsm), *.xlsm,Excel Workbook (*.xlsx), *.xlsx")
If result = False Then Exit Sub
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs result
End Sub