VBA Date Functions
Written by
Reviewed by
In this Article
- Dates in VBA
- DateSerial Function
- DateValue Function
- VBA DatePart Function
- Referencing Dates
- Using Different Units of Interval
- VBA Date Function
- VBA Now Function
- VBA Time Function
- VBA DateAdd Function
- VBA DateDiff Function
- VBA Day Function
- VBA Hour Function
- VBA Minute Function
- VBA Second Function
- VBA Month Function
- VBA MonthName Function
- VBA TimeSerial Function
- VBA TimeValue Function
- VBA Weekday Function
- VBA WeekdayName Function
- VBA Year Function
- Comparing Dates in VBA
- IsDate Function
This tutorial will cover how to work with dates in VBA.
Dates in VBA
In Excel (and VBA), Dates are stored as integer values.
Day 1 in the world of Excel was the 1st January 1900 (Windows default) or 1st January 1904 (Macintosh default) – which means that the 5th August 2021 is day 44413. 44413.456 is 10.56am on the 5th August 2021 where 44413.5 will be exactly 12 noon.
In Excel, DateTimes are then formatted to show as a date.
There are several ways to refer to Dates in VBA:
DateSerial Function
The DateSerial Function returns a date from a provided Year, Month, and Day:
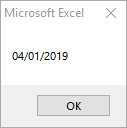
Sub DateSerial_Example()
MsgBox DateSerial(2019, 4, 1)
End SubThis code will return 04/01/2019.
You can also enter negative values to move backwards in time:
MsgBox DateSerial(2019, -5, 10)Result: 07/10/2018
DateValue Function
The DateValue Function returns an integer corresponding to a Date:
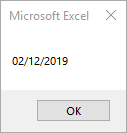
Sub DateValue_Example()
MsgBox DateValue("Feb 12, 2019")
End SubThis code will return 02/12/2019.
The following examples will have same result.
DateValue("2 12 2019")
DateValue("2/12/2019")
DateValue("2,12,2019")
DateValue("2-12-2019")
DateValue("February 12, 2019")
DateValue("Feb/12/2019")
If date is a string that includes only numbers separated by valid date seperators(” “, “/”, “,”, “-“), DateValue recognizes the order for month, day, and year according to the Short Date format that you specified for your system. DateValue also recognizes unambiguous dates that contain month names, either in long or abbreviated form.
If the year part of date is omitted, DateValue uses the current year from your computer’s system date.
If the date argument includes time information, DateValue doesn’t return it. However, if date includes invalid time information (such as “37:69”), an error occurs.
This example will reference a cell containing a date:
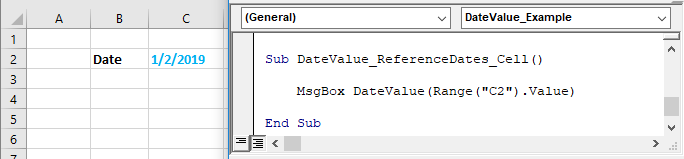
Sub DateValue_ReferenceDates_Cell()
MsgBox DateValue(Range("C2").Value)
End SubThis will return 01/02/2019.
VBA DatePart Function
The DatePart Function works in reverse of the DateSerial Function. It will output a part of a date (year, month, day, etc.) from a date serial:
Sub DatePart_Year_Test()
MsgBox DatePart("yyyy", #1/1/2019#)
End SubThis code will return 2019.

The DatePart Function contains 4 arguments:
Interval: Time unit (Days, Months, Years, etc.). Enter as string. (ex. “m” for Month)
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| yyyy | Year |
| q | Quarter |
| m | Month |
| y | Day of Year |
| d | Day |
| w | Weekday |
| ww | Week |
| h | Hour |
| n | Minute |
| s | Second |
Date: Varient (Date) value that you want to evaluate.
FirstDayOfWeek: A constant that specifies the first day of the week. This is optional. If not specified, Sunday is assumed.
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| vbUseSystem | 0 | Use the NLS API setting. |
| vbSunday | 1 | Sunday (default) |
| vbMonday | 2 | Monday |
| vbTuesday | 3 | Tuesday |
| vbWednesday | 4 | Wednesday |
| vbThursday | 5 | Thursday |
| vbFriday | 6 | Friday |
| vbSaturday | 7 | Saturday |
FirstWeekOfYear: A constant that specifies the first week of the year. This is optional. If not specified, the first week is assumed to be the week in which January 1 occurs.
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| vbUseSystem | 0 | Use the NLS API setting. |
| vbFirstJan1 | 1 | Start with week in which January 1 occurs (default). |
| vbFirstFourDays | 2 | Start with the first week that has at least four days in the new year. |
| vbFirstFullWeek | 3 | Start with first full week of the year. |
Referencing Dates
To start, we will demonstrate different ways to reference dates using the VBA DatePart Function.
Each of these DatePart functions produce the same result:
Sub DateAdd_ReferenceDates()
MsgBox DatePart("yyyy", #4/1/2019#)
MsgBox DatePart("yyyy", DateSerial(2019, 4, 1))
MsgBox DatePart("yyyy", DateValue("April 1, 2019"))
End SubOr you can reference a cell containing a date:
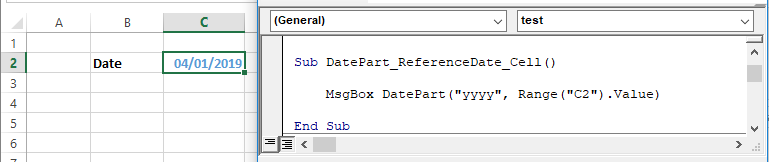
Sub DatePart_ReferenceDate_Cell()
MsgBox DatePart("yyyy", Range("C2").Value)
End SubOr create and reference date variables:
Sub DatePart_Variable()
Dim dt As Date
dt = #4/1/2019#
MsgBox DateAdd("yyyy", dt)
End Sub
Using Different Units of Interval
Quarter
Sub DatePart_Quarter()
MsgBox DatePart("q", #6/30/2019#)
End SubMonth
Sub DatePart_Month()
MsgBox DatePart("m", #6/30/2019#)
' equivalent
MsgBox Month(#6/30/2019#)
End SubDay
Sub DatePart_Day()
MsgBox DatePart("d", #6/30/2019#)
' equivalent
MsgBox Day(#6/30/2019#)
End SubWeek
Sub DatePart_Week_Test()
MsgBox DatePart("w", #6/30/2019#)
' equivalent
MsgBox Weekday(#6/30/2019#)
End SubHour
Sub DatePart_Hour()
Dim dt As Date
Dim nHour As Long
dt = #8/14/2019 9:30:00 AM#
nHour = DatePart("h", dt)
MsgBox nHour
' equivalent
MsgBox Hour(dt)
End SubMinutes
Sub DatePart_Minute()
MsgBox DatePart("n", #8/14/2019 9:15:00 AM#)
' equivalent
MsgBox Minute(#8/14/2019 9:15:00 AM#)
MsgBox Minute(#9:15:00 AM#)
End SubSecond
Sub DatePart_Second()
MsgBox DatePart("s", #8/14/2019 9:15:15 AM#)
' equivalent
MsgBox Second(#8/14/2019 9:15:15 AM#)
MsgBox Second(#9:15:15 AM#)
End SubVBA Date Function
You can use the Date Function to return the current date.
The syntax of the Date Function is Date(). It has no arguments.
The following code shows you how to use the Date Function:
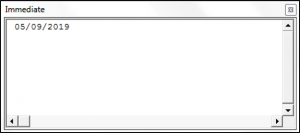
Sub UsingTheDateFunction()
Dim theDate As Date
theDate = Date()
Debug.Print theDate
End SubThe result shown in the Immediate Window is:
VBA Now Function
You can use the Now Function to return the current date and time.
The syntax of the Now Function is Now(). It has no arguments.
The following code shows you how to use the Now Function:
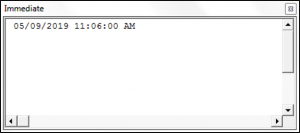
Sub UsingTheNowFunction()
Dim theDate As Date
theDate = Now()
Debug.Print theDate
End SubThe result is:
VBA Time Function
You can use the Time Function to return the current time.
The syntax of the Time Function is Time(). It has no arguments.
The following code shows you how to use the Time Function:
Sub UsingTheTimeFunction()
Dim theTime As Date
theTime = Time()
Debug.Print theTime
End SubThe result is:

VBA DateAdd Function
You can use the DateAdd Function to add a date/time interval to a date or time, and the function will return the resulting date/time.
The syntax of the DateAdd Function is:
DateAdd(Interval, Number, Date) where:
- Interval – A string that specifies the type of interval to use. The interval can be one of the following values:
“d” – day
“ww” – week
“w” – weekday
“m” – month
“q” – quarter
“yyyy” – year
“y” – day of the year
“h” – hour
“n” – minute
“s” – second
- Number – The number of intervals that you want to add to the original date/time.
- Date – The original date/time.
Note: When using dates in your code you have to surround them with # or quotation marks.
The following code shows how to use the DateAdd Function:
Sub UsingTheDateAddFunction()
Dim laterDate As Date
laterDate = DateAdd("m", 10, "11/12/2019")
Debug.Print laterDate
End SubThe result is:

VBA DateDiff Function
You can use the DateDiff Function in order to get the difference between two dates, based on a specified time interval.
The syntax of the DateDiff Function is:
DateDiff(Interval, Date1, Date2, [Firstdayofweek], [Firstweekofyear]) where:
- Interval – A string that specifies the type of interval to use. The interval can be one of the following values:
“d” – day
“ww” – week
“w” – weekday
“m” – month
“q” – quarter
“yyyy” – year
“y” – day of the year
“h” – hour
“n” – minute
“s” – second
- Date1 – A date value representing the earlier date.
- Date2 – A date value representing the later date.
- Firstdayofweek (Optional) – A constant that specifies the weekday that the function should use as the first day of the week. If blank Sunday is used as the first day of the week. Firstdayofweek can be one of the following values:
-vbSunday – uses Sunday as the first day of the week.
-vbMonday – uses Monday as the first day of the week.
-vbTuesday – uses Tuesday as the first day of the week.
-vbWednesday – uses Wednesday as the first day of the week.
-vbThursday – uses Thursday as the first day of the week.
-vbFriday – uses Friday as the first day of the week.
-vbSaturday – uses Saturday as the first day of the week.
-vbUseSystemDayOfTheWeek – uses the first day of the week that is specified by your system’s settings.
- Firstweekofyear (Optional) – A constant that specifies the first week of the year. If blank then the Jan 1st week is used as the first week of the year. Firstweekofyear can be one of the following values:
-vbFirstJan1 – uses the week containing Jan 1st.
-vbFirstFourDays – uses the first week that contains at least four days in the new year.
-vbFirstFullWeek – uses the first full week of the year.
-vbSystem – uses the first week of the year as specified by your system settings.
The following code shows you how to use the DateDiff Function:
Sub UsingTheDateDiffFunction()
Dim theDifferenceBetweenTwoDates As Long
theDifferenceBetweenTwoDates = DateDiff("q", "11/11/2010", "10/12/2012")
Debug.Print theDifferenceBetweenTwoDates
End SubThe result is:
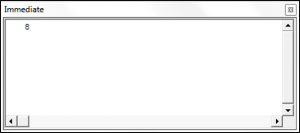
VBA Day Function
You can use the Day Function to return the day of an input date.
The syntax of the Day Function is:
Day(Date_value) where:
- Date_value – The date which you want to extract the day from.
The following code shows you how to use the Day Function:
Sub UsingTheDayFunction()
Dim theDay As Integer
theDay = Day("10/12/2010")
Debug.Print theDay
End SubThe result is:
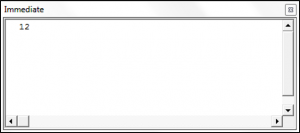
VBA Hour Function
You can use the Hour Function to return the hour of an input time.
The syntax of the Hour Function is:
Hour(Time) where:
- Time – The time that you want to extract the hour from.
The following code shows you how to use the Hour Function:
Sub UsingTheHourFunction()
Dim theHour As Integer
theHour = Hour("2:14:17 AM")
Debug.Print theHour
End SubThe result is:

VBA Minute Function
You can use the Minute Function to return the minute value of an input time.
The syntax of the Minute Function is:
Minute(Time) where:
- Time – The time that you want to extract the minute value from.
The following code shows you how to use the Minute Function:
Sub UsingTheMinuteFunction()
Dim theMinuteValue As Integer
theMinuteValue = Minute("2:14:17 AM")
Debug.Print theMinuteValue
End SubThe result is:
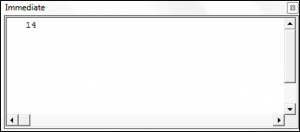
VBA Second Function
You can use the Second Function to return the second value of an input time.
The syntax of the Second Function is:
Second(Time) where:
- Time – The time that you want to extract the second value from.
The following code shows you how to use the Second Function:
Sub UsingTheSecondFunction()
Dim theSecondValue As Integer
theSecondValue = Second("2:14:17 AM")
Debug.Print theSecondValue
End SubThe result is:
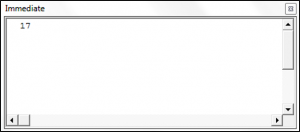
VBA Month Function
You can use the Month Function to return the month of an input date.
The syntax of the Month Function is:
Month(Date_value) where:
- Date_value – The date which you want to extract the month from.
The following code shows you how to use the Month Function:
Sub UsingTheMonthFunction()
Dim theMonth As Integer
theMonth = Month("11/18/2010")
Debug.Print theMonth
End SubThe result is:
More examples of the VBA Month function:
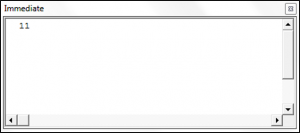
MsgBox Month(#5/14/2019 5:25:00 AM#)Result: 5
MsgBox Month("8/14/2019 15:33:00")Result: 8
MsgBox Month("11/14/2019")Result: 11
MsgBox Month(Now)Result will be the month of the current system date.
VBA MonthName Function
You can use the MonthName Function to return the name of a month from an input supplied month number.
The syntax of the MonthName Function is:
MonthName(Number_of_month, [Abbreviate]) where:
- Number_of_month – An integer value between 1 and 12.
- Abbreviate (Optional) – Specifies whether the month name should be abbreviated. If blank the default value of False is used.
Sub UsingTheMonthNameFunction()
Dim theMonthName As String
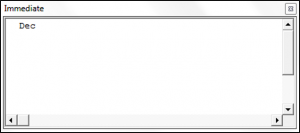
theMonthName = MonthName(12, True)
Debug.Print theMonthName
End SubThe result is:
More Examples:
MsgBox MonthName(2)
Result: “February”
MsgBox MonthName(2, True)Result: “Feb”
MsgBox MonthName(9, False)Result: “September”
VBA TimeSerial Function
The TimeSerial Function takes an input hour, minute and second and returns a time.
The syntax of the TimeSerial Function is:
TimeSerial(Hour, Minute, Second) where:
- Hour – An integer value between 0 and 23 that represents the hour value.
- Minute – An integer value between 0 and 59 that represents the minute value.
- Second – An integer value between 0 and 59 that represents the second value.
The following code shows you how to use the TimeSerial Function:
Sub UsingTheTimeSerialFunction()
Dim theTime As Date
theTime = TimeSerial(1, 10, 15)
Debug.Print theTime
End SubThe result is:

VBA TimeValue Function
The TimeValue Function returns a Time from a string representation of a date or time.
The syntax of the TimeValue Function is:
TimeValue(Time) where:
- Time – A String representing the time.
The following code shows you how to use the TimeValue Function:
Sub UsingTheTimeValueFunction()
Dim theTime As Date
theTime = TimeValue("22:10:17")
Debug.Print theTime
End SubThe result is:

VBA Weekday Function
You can use the Weekday Function to return an integer from 1 – 7 representing a day of the week for a date.
The syntax of the Weekday Function is:
Weekday(Date, [Firstdayofweek]) where:
- Date – The date that you want to extract the weekday value from.
- Firstdayofweek (Optional) – A constant that specifies the weekday that the function should use as the first day of the week. If blank Sunday is used as the first day of the week. Firstdayofweek can be one of the following values:
-vbSunday – uses Sunday as the first day of the week.
-vbMonday – uses Monday as the first day of the week.
-vbTuesday – uses Tuesday as the first day of the week.
-vbWednesday – uses Wednesday as the first day of the week.
-vbThursday – uses Thursday as the first day of the week.
-vbFriday – uses Friday as the first day of the week.
-vbSaturday – uses Saturday as the first day of the week.
-vbUseSystemDayOfTheWeek – uses the first day of the week that is specified by your system’s settings.
The following code shows you how to use the Weekday Function:
Sub UsingTheWeekdayFunction()
Dim theWeekDay As Integer
theWeekDay = Weekday("11/20/2019")
Debug.Print theWeekDay
End SubThe result is:

Here are some more examples of Weekday:
MsgBox Weekday("1/1/2019", vbMonday)Result: 2
MsgBox Weekday("1/1/2019", vbTuesday)Result: 1
MsgBox Weekday("1/1/2019", vbFriday)Result: 5
VBA WeekdayName Function
You can use the WeekdayName Function to return the name of a weekday from an input supplied weekday number.
The syntax of the WeekdayName Function is:
WeekdayName(Weekday, [Abbreviate], [Firstdayoftheweek]) where:
- Weekday – An integer value between 1 and 7.
- Abbreviate (Optional) -Specifies whether the weekday name should be abbreviated. If blank the default value of False is used.
- Firstdayofweek (Optional) – A constant that specifies the weekday that the function should use as the first day of the week. If blank Sunday is used as the first day of the week. Firstdayofweek can be one of the following values:
-vbSunday – uses Sunday as the first day of the week.
-vbMonday – uses Monday as the first day of the week.
-vbTuesday – uses Tuesday as the first day of the week.
-vbWednesday – uses Wednesday as the first day of the week.
-vbThursday – uses Thursday as the first day of the week.
-vbFriday – uses Friday as the first day of the week.
-vbSaturday – uses Saturday as the first day of the week.
-vbUseSystemDayOfTheWeek – uses the first day of the week that is specified by your system’s settings.
Sub UsingTheWeekdayNameFunction()
Dim theWeekdayName As String
theWeekdayName = WeekdayName(4)
Debug.Print theWeekdayName
End SubThe result is:

VBA Year Function
You can use the Year Function to return the year of an input date.
The syntax of the Year Function is:
Year(Date_value) where:
- Date_value – The date which you want to extract the year from.
The following code shows you how to use the Year Function:
Sub UsingTheYearFunction()
Dim theYear As Integer
theYear = Year("11/12/2010")
Debug.Print theYear
End SubThe result is:

More Examples:
MsgBox Year("1/1/1999")Result: 1999
MsgBox Year(#1/1/2001 1:30:00 AM#)Result: 2001
MsgBox Year("1/1/05")Result: 1905
MsgBox Year(Date)Result will be the year of the current system date.
Sub Year_Example()
MsgBox Year("1/1/2019")
End SubThis code will return 2019.

Comparing Dates in VBA
You can compare dates using the >, <, and = operators in VBA. The following code shows you how to compare two dates in VBA.
Sub ComparingDates()
Dim dateOne As Date
Dim dateTwo As Date
dateOne = "10/10/2010"
dateTwo = "11/11/2010"
If dateOne > dateTwo Then
Debug.Print "dateOne is the later date"
ElseIf dateOne = dateTwo Then
Debug.Print "The two dates are equal"
Else
Debug.Print "dateTwo is the later date"
End If
End Sub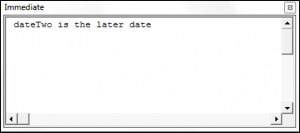
Learn more about how to Format dates as strings by viewing this tutorial.
IsDate Function
IsDate will test if an expression is a valid date and return TRUE or FALSE.
Examples:
Sub IsDate_Example()
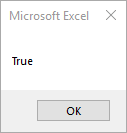
MsgBox IsDate("4/12/2019")
End SubThis will return True.
MsgBox IsDate("4\12\2019")This will return false because the slashes are backwards.
More Valid Dates:
MsgBox IsDate("8/22/2019")
MsgBox IsDate("8 22 19")
MsgBox IsDate("Aug 22 19")
MsgBox IsDate("8,22,2019")
MsgBox IsDate("8-22-19")
MsgBox IsDate("8/22")
MsgBox IsDate("8-22")
Result: True
Invalid Dates:
MsgBox IsDate("8.22.2019")
MsgBox IsDate("8\22\2019")
MsgBox IsDate("Aug")
MsgBox IsDate("2019")
Result: False