VBA Cell Value – Get, Set, or Change
Written by
Reviewed by
In this Article
This tutorial will teach you how to interact with Cell Values using VBA.
Set Cell Value
To set a Cell Value, use the Value property of the Range or Cells object.
Range.Value & Cells.Value
There are two ways to reference cell(s) in VBA:
- Range Object – Range(“A2”).Value
- Cells Object – Cells(2,1).Value
The Range object allows you to reference a cell using the standard “A1” notation.
This will set the range A2’s value = 1:
Range("A2").Value = 1The Cells object allows you to reference a cell by it’s row number and column number.
This will set range A2’s value = 1:
Cells(2,1).Value = 1Notice that you enter the row number first:
Cells(Row_num, Col_num)Set Multiple Cells’ Values at Once
Instead of referencing a single cell, you can reference a range of cells and change all of the cell values at once:
Range("A2:A5").Value = 1Set Cell Value – Text
In the above examples, we set the cell value equal to a number (1). Instead, you can set the cell value equal to a string of text. In VBA, all text must be surrounded by quotations:
Range("A2").Value = "Text"If you don’t surround the text with quotations, VBA will think you referencing a variable…
Set Cell Value – Variable
You can also set a cell value equal to a variable
Dim strText as String
strText = "String of Text"
Range("A2").Value = strTextGet Cell Value
You can get cell values using the same Value property that we used above.
Get ActiveCell Value
To get the ActiveCell value and display it in a message box:
MsgBox ActiveCell.ValueAssign Cell Value to Variable
To get a cell value and assign it to a variable:
Dim var as Variant
var = Range("A1").ValueHere we used a variable of type Variant. Variant variables can accept any type of values. Instead, you could use a String variable type:
Dim var as String
var = Range("A1").ValueA String variable type will accept numerical values, but it will store the numbers as text.
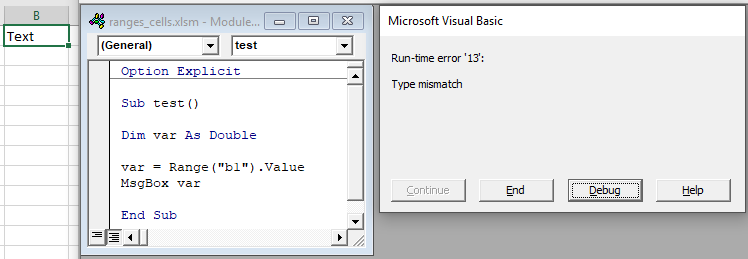
If you know your cell value will be numerical, you could use a Double variable type (Double variables can store decimal values):
Dim var as Double
var = Range("A1").ValueHowever, if you attempt to store a cell value containing text in a double variable, you will receive an type mismatch error:
Other Cell Value Examples
Copy Cell Value
It’s easy to set a cell value equal to another cell value (or “Copy” a cell value):
Range("A1").Value = Range("B1").ValueYou can even do this with ranges of cells (the ranges must be the same size):
Range("A1:A5").Value = Range("B1:B5").ValueCompare Cell Values
You can compare cell values using the standard comparison operators.
Test if cell values are equal:
MsgBox Range("A1").Value = Range("B1").ValueWill return TRUE if cell values are equal. Otherwise FALSE.
You can also create an If Statement to compare cell values:
If Range("A1").Value > Range("B1").Value Then
Range("C1").Value = "Greater Than"
Elseif Range("A1").Value = Range("B1").Value Then
Range("C1").Value = "Equal"
Else
Range("C1").Value = "Less Than"
End IfYou can compare text in the same way (Remember that VBA is Case Sensitive)