VBA Add Sheet and Name the Sheet
Written by
Reviewed by
In this Article
This tutorial will cover how to add/insert worksheets using VBA.
Add Worksheet
This simple macro will add a sheet before the ActiveSheet:
Sub Add ()
Sheets.Add
End SubAfter you insert a worksheet, the new worksheet becomes the ActiveSheet. You can then use the ActiveSheet object to work with the new sheet (at the end of this article, we will show you how to insert a new sheet directly into a variable).
ActiveSheet.Name = "NewSheet"Add a sheet with a name
You can also define a worksheet name when creating the new sheet:
Sheets.Add.Name = "NewSheet"Create new worksheet with name from a cell
Or use a cell value to name a new worksheet:
Sheets.Add.Name = range("a3").valueAdd worksheet before / after another worksheet
You may also want to choose the location where the new sheet is inserted. You can use the After or Before properties to insert a worksheet in a specific location in your workbook.
Insert worksheet after another worksheet
This code will insert the new worksheet AFTER another worksheet:
Sheets.Add After:=Sheets("Input")This will insert a new worksheet AFTER another worksheet and specify the name of the worksheet:
Sheets.Add(After:=Sheets("Input")).Name = "NewSheet"Note the extra parenthesis needed in the second example (the first example will generate an error if the second parenthesis is added).
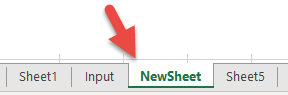
or Before:
Sheets.Add(Before:=Sheets("Input")).Name = "NewSheet"In these examples, we explicitly name the worksheet used to determine the location of the worksheet. Often, you will want to use the index number of the worksheet instead, so you can insert the worksheet at the beginning or end of the workbook:
Add worksheet to end of workbook
To add a worksheet to the end of the workbook:
Sheets.Add After:=Sheets(Sheets.Count)Add Sheet To Beginning of Workbook:
To add a sheet to the beginning of the workbook:
Sheets.Add(Before:=Sheets(1)).Name = "FirstSheet"Add sheet to variable
This code assigns the new sheet to a variable as the sheet is created:
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Sheets.AddFrom here, you can reference the new worksheet with the variable ‘ws’:
ws.name = "VarSheet"More examples of adding a worksheet
Create sheet if it doesn’t exist yet
You might want to create a sheet only if it doesn’t already exist.
Creating worksheets from a list of names
The following routine will examine the contents of a single column and create Excel worksheets in the current workbook with those names. It makes a call to another function to check if a sheet with that name already exists and if it does, the sheet will not be created.
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Call CreateWorksheets(Sheets("Sheet2").Range("A1:a10"))
End Sub
Sub CreateWorksheets(Names_Of_Sheets As Range)
Dim No_Of_Sheets_to_be_Added As Integer
Dim Sheet_Name As String
Dim i As Integer
No_Of_Sheets_to_be_Added = Names_Of_Sheets.Rows.Count
For i = 1 To No_Of_Sheets_to_be_Added
Sheet_Name = Names_Of_Sheets.Cells(i, 1).Value
'Only add sheet if it doesn't exist already and the name is longer than zero characters
If (Sheet_Exists(Sheet_Name) = False) And (Sheet_Name <> "") Then
Worksheets.Add().Name = Sheet_Name
End If
Next i
End SubFunction Sheet_Exists(WorkSheet_Name As String) As Boolean
Dim Work_sheet As Worksheet
Sheet_Exists = False
For Each Work_sheet In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
If Work_sheet.Name = WorkSheet_Name Then
Sheet_Exists = True
End If
Next
End FunctionSo if we have the following text in cells A1:A30 in Sheet 2:
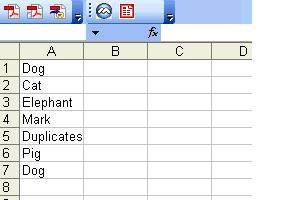
The following worksheets will be created:
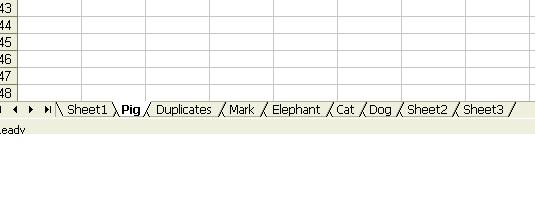
Note that although “Dog” appears twice, only one worksheet is created.
To download the .XLS file for this tutorial, click here.
VBA coding made easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro – a VBA code builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!