DDB Function Examples – Excel, VBA, & Google Sheets
Written by
Reviewed by
This tutorial demonstrates how to use the Excel DDB Function in Excel to calculate the depreciation of an asset.
DDB Function Overview
The DDB Function Calculates the depreciation value.
To use the DDB Excel Worksheet Function, select a cell and type:
![]()
(Notice how the formula inputs appear)
DDBFunction Syntax and Inputs:
=DDB(cost,salvage,life,period,[factor])cost – It’s the initial cost price of the asset.
salvage – It’s the remaining value of the asset after its useful life. This value can be zero.
life – It’s the number of periods after which the asset is fully deprecated. It’s also known as the useful life of the asset.
period – It’s the specified period over which the depreciation is to be calculated.
factor – OPTIONAL: It’s the rate at which the balance declines. If its value is omitted, it takes the value of 2 as default.
What Is DDB?
Double Declining Balance Depreciation Method is a type of an accelerated depreciation method in which the asset value is depreciated two times faster than the rate of the straight-line depreciation method.
Double Declining Balance Method is calculated using the following equation:
DDB = 2*SLDR*BVAWhere:
SLDR = Straight-line Depreciation Rate
BVA = Book Value of an Asset
What is the Excel DDB Function?
The Excel DDB function calculates the depreciation of an asset for a specified period using the double-declining balance method or another specified method.
It is an accelerated depreciation calculation. That means the asset value is depreciated higher in its initial period and lower in successive periods.
The DDB function uses the following formula to calculate the depreciation value of an asset:
=MIN((cost-pd)*(factor/life),(cost-salvage-pd))Where
pd = Total Depreciation in all prior periods
Calculate Depreciation value of a car
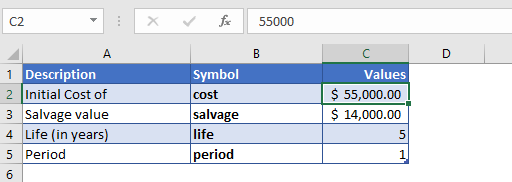
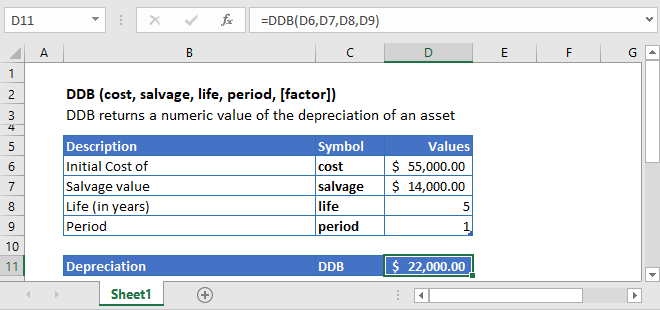
Let’s calculate the depreciation value of a car in its first year. The total cost of a car is $55,000 and after five years of usage, it has a resale value of $14,000.
The depreciation value of the car during its first year is calculated using the following formula:
=DDB(C4,C5,C6,C7)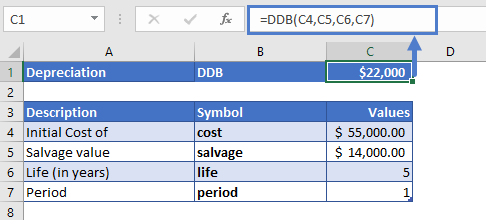
The declining balance depreciation for its first year is calculated as
DDB = $22,000
Calculate Depreciation value of a Machinery during its life
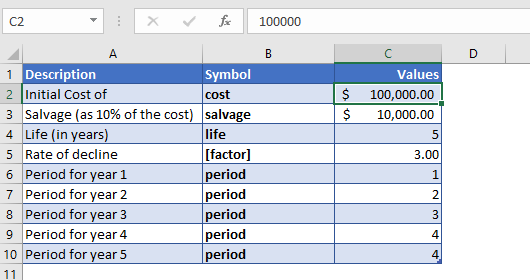
Suppose a company bought machinery at a cost of $100,000. The machinery has a useful life of five years and a salvage value of $10,000. Now we’ll calculate the depreciation value of the machinery at each year up to its useful life at triple declining balance depreciation.
To calculate the depreciation of the machinery, we’ll use the following formula:
=DDB($C$2,$C$3,$C$4,C6,$C$5)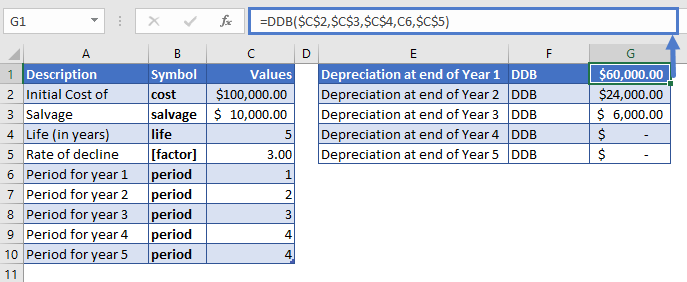
The depreciation values of the machinery over its life are mentioned in the right table.
Here, we have used absolute cell reference (press the F4 key to make a cell reference absolute) for the values of cost, salvage, life, and factor.
Under the value of factor 3, the depreciation expense is so accelerated that by the end of year 3, the machinery is fully depreciated. However, the excel didn’t depreciate the machinery to a value lower than its salvage value.
Additional Notes
The unit of life and period arguments must be the same.
All the five arguments of the DDB function should have positive values.
#NUM! Error occurs if the supplied salvage or cost value is less than zero; or the supplied life, period, or [factor] arguments’ values are less than and equal to zero ( ≤ 0 ); or the supplied period value is greater than life arguments’ value.
#VALUE! Error occurs if any of the arguments are non-numeric.
Return to the List of all Functions in Excel
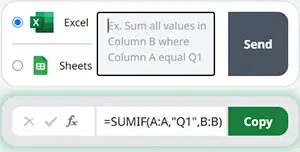
DDB in Google Sheets
All of the above examples work exactly the same in Google Sheets as in Excel.
DDB Examples in VBA
You can also use the DDB function in VBA. Type:
application.worksheetfunction.ddb(cost,salvage,life,period,factor)For the function arguments (cost, etc.), you can either enter them directly into the function or define variables to use instead.