DAYS360 Function – Examples in Excel, VBA, Google Sheets
Written by
Reviewed by
Download the example workbook
This tutorial demonstrates how to use the Excel DAYS360 Function in Excel to count the number of days between dates.
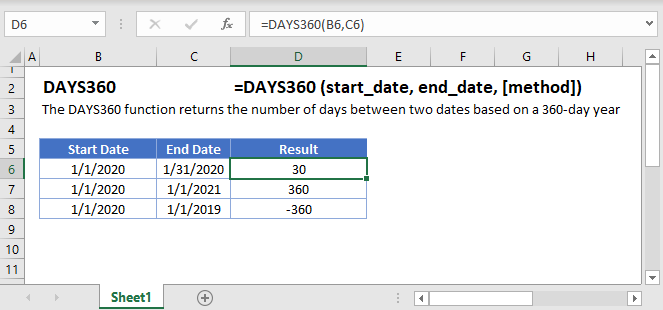
Calculate Number of Days Between Dates (Based on 360-day Year)
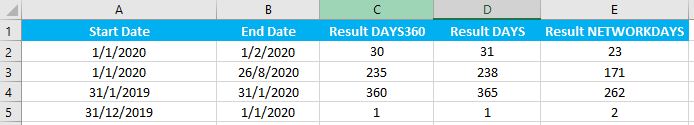
The DAYS360 function returns the number of days between two dates based on a 360-day year where each month is considered to have 30 days. To calculate the actual number of days between dates, use the DAYS Function. Note the differences below:
=DAYS(C3,B3)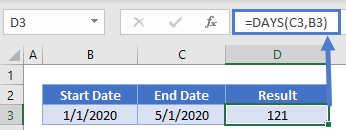 Notice the DAYS360 function assumes each month has 30 days, so the difference is calculated as 4 months * 30 days/month = 120 days.
Notice the DAYS360 function assumes each month has 30 days, so the difference is calculated as 4 months * 30 days/month = 120 days.
=DAYS360(B3,C3)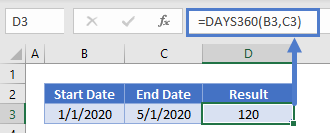 The DAYS360 Function allows you to switch between the Default US method (FALSE), and the European method (TRUE):
The DAYS360 Function allows you to switch between the Default US method (FALSE), and the European method (TRUE):
=DAYS360(B3,C3,FALSE)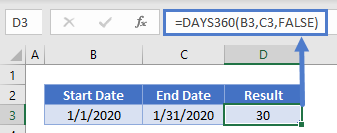
=DAYS360(B3,C3,TRUE)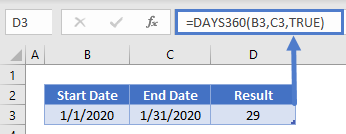
Days From Today (360)
This example will show how to calculate the number of days from a date to today using the 360-day year:
=DAYS360(TODAY(),B3)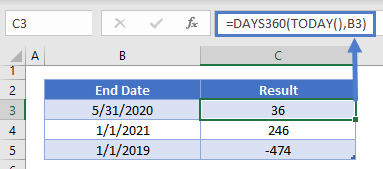 This example also makes use of the TODAY Function.
This example also makes use of the TODAY Function.
NETWORKINGDAYS
The NETWORKINGDAYS Function will calculate the number of business days between dates:
=NETWORKDAYS(B3,C3)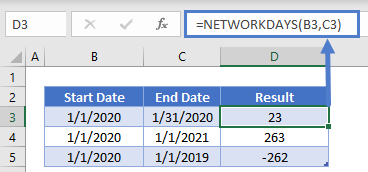 DAYS360 in Google Sheets
DAYS360 in Google Sheets
The DAYS360 Function works exactly the same in Google Sheets as in Excel:
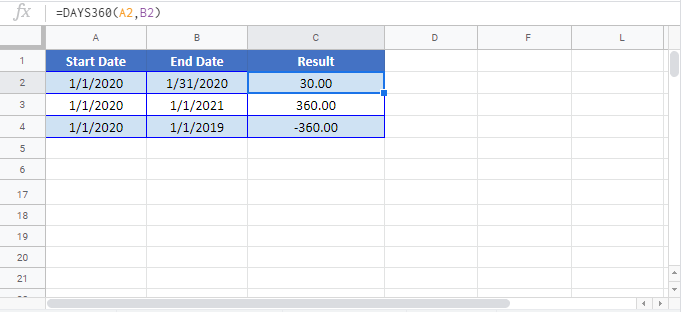
DAYS360 Examples in VBA
You can also use the DAYS360 function in VBA. Type:
application.worksheetfunction.days360(start_date,end_date,method)For the function arguments (start_date, etc.), you can either enter them directly into the function, or define variables to use instead.
Executing the following VBA statements
Range("C2") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Days360(Range("A2"), Range("B2"), False)
Range("C3") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Days360(Range("A3"), Range("B3"), False)
Range("C4") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Days360(Range("A4"), Range("B4"), False)
Range("C5") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Days360(Range("A5"), Range("B5"), False)
Range("D2") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Days(Range("B2"), Range("A2"))
Range("D3") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Days(Range("B3"), Range("A3"))
Range("D4") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Days(Range("B4"), Range("A4"))
Range("D5") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Days(Range("B5"), Range("A5"))
Range("E2") = Application.WorksheetFunction.NetworkDays(Range("A2"), Range("B2"))
Range("E3") = Application.WorksheetFunction.NetworkDays(Range("A3"), Range("B3"))
Range("E4") = Application.WorksheetFunction.NetworkDays(Range("A4"), Range("B4"))
Range("E5") = Application.WorksheetFunction.NetworkDays(Range("A5"), Range("B5"))will produce the following results: