CLEAN Function – Clean Text – Excel, VBA & Google Sheets
Written by
Reviewed by
Download the example workbook
This tutorial demonstrates how to use the CLEAN Function in Excel to remove all non-printable characters.
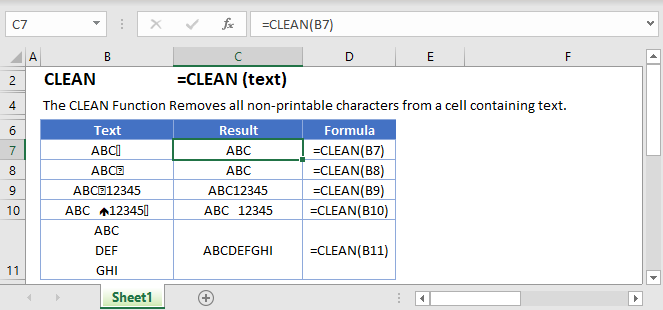
How to use the CLEAN Function:
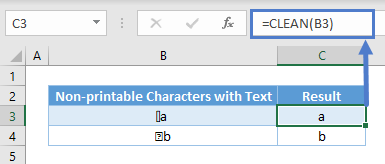
The CLEAN function removes all non-printable from ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) character 0 to 31. One example of it is removing line breaks.
=CLEAN(B3)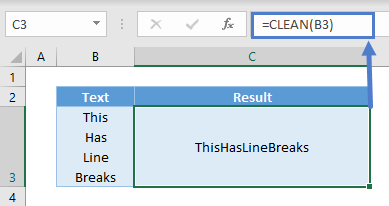
Other Non-Printable Characters
All of our characters in the keyboard have a specific ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) code to it. You could use CODE to find out what is the ASCII code of the character. Some of the unprintable ones from 1 to 31 are these below you can remove with CLEAN:
If you test out the ASCII code numbers, you will see that many of them look identical. They are not meant to be used in Excel but for other programs.
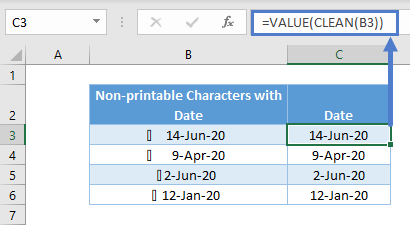
CLEAN with Numbers and Dates
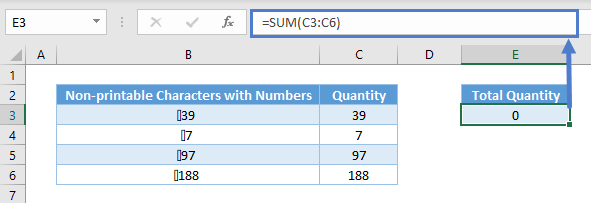
Do note that CLEAN is a text function. Upon using CLEAN, the result is a text. For instance, you won’t be able to sum up these numbers in cell E3 after using CLEAN.
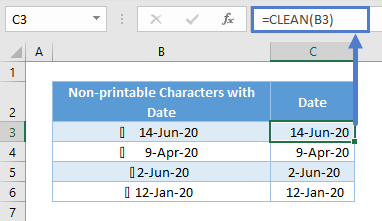
The same thing happens for dates as they are recognized as serial numbers and not text. You may not need to sum dates, but it doesn’t work well in filters and PivotTables.
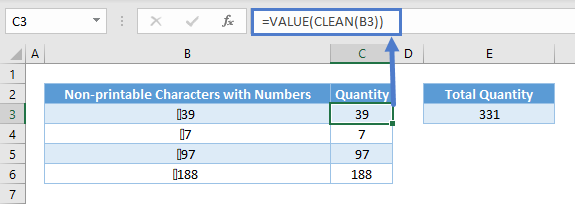
To overcome the issues above, you can use VALUE to convert from text to values.
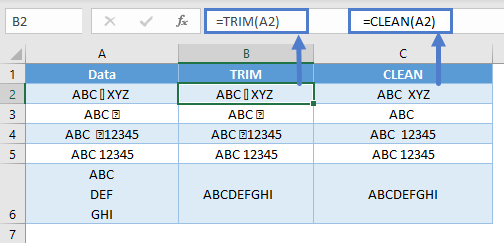
CLEAN VS TRIM
CLEAN function applicable only for non-printable characters, so if you need to remove space and other characters you need to use TRIM. refer below table to get idea about different between TRIM and CLEAN
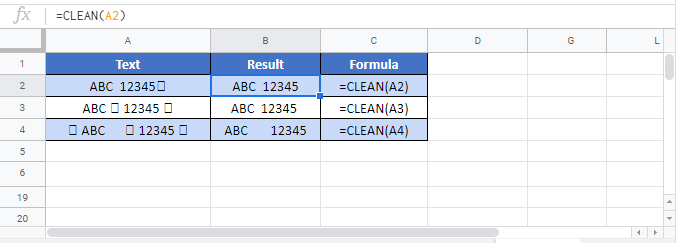
CLEAN in Google Sheets
The CLEAN Function works exactly the same in Google Sheets as in Excel:
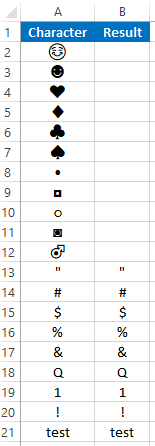
CLEAN Examples in VBA
You can also use the CLEAN function in VBA. Type:
application.worksheetfunction.clean(text)Executing the following VBA statements
Range("B2") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Clean(Range("A2"))
Range("B3") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Clean(Range("A3"))
Range("B4") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Clean(Range("A4"))
Range("B5") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Clean(Range("A5"))
Range("B6") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Clean(Range("A6"))
Range("B7") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Clean(Range("A7"))
Range("B8") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Clean(Range("A8"))
Range("B9") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Clean(Range("A9"))
Range("B10") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Clean(Range("A10"))
Range("B11") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Clean(Range("A11"))
Range("B12") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Clean(Range("A12"))
Range("B13") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Clean(Range("A13"))
Range("B14") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Clean(Range("A14"))
Range("B15") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Clean(Range("A15"))
Range("B16") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Clean(Range("A16"))
Range("B17") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Clean(Range("A17"))
Range("B18") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Clean(Range("A18"))
Range("B19") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Clean(Range("A19"))
Range("B20") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Clean(Range("A20"))
Range("B21") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Clean(Range("A21"))will produce the following results
For more information about the CLEAN Formula visit the Microsoft Website.